Prostatitis is an inflammatory process located in the prostate. This pathology is very common and is usually diagnosed during the reproductive age of men. The prostate (the second name for the prostate) is located under the bladder and partially surrounds the urethra (urethra). Therefore, even minor dysfunction of this organ can lead to dysfunction of the genitourinary system.
Causes of the development of prostatitis
Prostatitis is classified as an inflammatory process, but this does not mean that it is entirely caused by pathogenic microorganisms. The doctor (andrologist is engaged in the research of male reproductive system diseases) identified several reasons for the development of related pathology:
- Blood stagnation in the small pelvis. This refers to the violation of the blood microcirculation of the prostate and nearby organs, causing the increase of organs. During the postoperative period, in the context of a sedentary lifestyle and obesity (not necessarily severe), violations may occur.
- Urogenital system infections. In most cases, when examining patients with prostatitis, doctors will isolate Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Staphylococcus, Chlamydia, and Trichomonas. In rare cases, the infection can penetrate the prostate against the background of a sore throat or flu-in this case, the inflammatory process in question is classified as a complication.
- Often causes trauma to the pelvic organs. For this reason, prostatitis will develop in drivers-they will constantly bear the load of the perineum, and the prostate will experience shaking and vibration.
- Bacteria enter through biological fluids. In everyone's body, there are bacterial communities in the intestines and urethra. Under normal conditions, they are absolutely harmless, and only under favorable conditions (weakened immune system, long-term use of drugs, chronic diseases, human immunodeficiency virus) can they cause disease and cause inflammatory processes. These bacteria can enter the prostate through blood or lymph.
In addition, when diagnosing the inflammatory process of the prostate, factors as pathological stimuli can also be considered:
- Frequent hypothermia-this may be due to the particularity of working conditions or ignoring the dressing rules for specific periods of the year;
- Endocrine system disorders-excessive or insufficient secretion of male hormones, diagnosed as diabetes;
- Sexual activity is too active, and long-term abstinence-the prostate is exhausted;
- Any chronic disease-in the context of untreated bronchitis, dental caries, cystitis, urinary tract infections, there are officially recorded cases of prostatitis development.
Symptoms of the inflammatory process
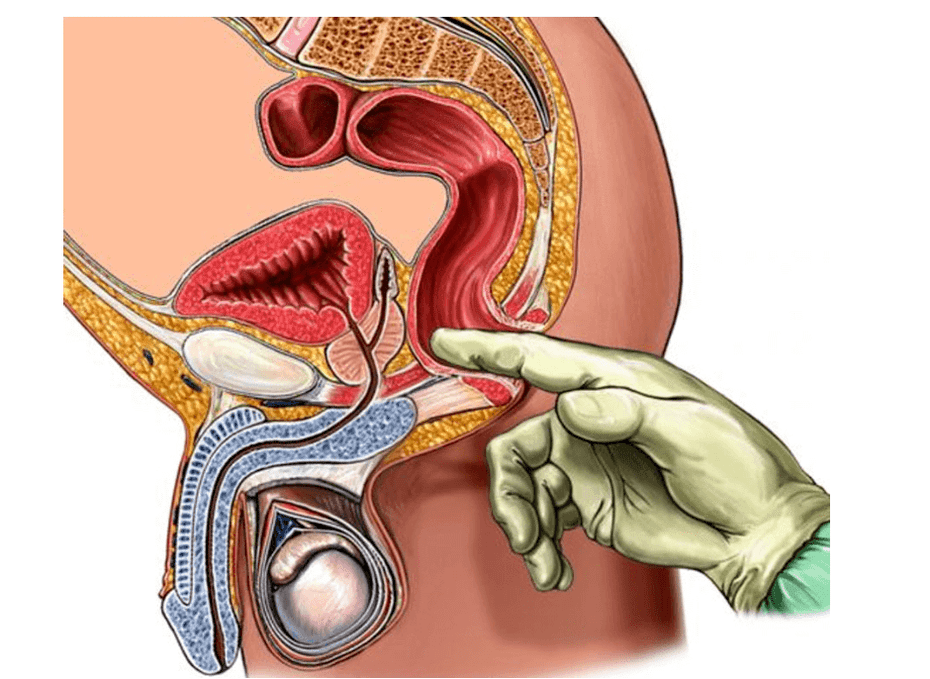
Andrologists distinguish between the main and indirect signs of the inflammatory process of the prostate. The main symptoms are obvious:
- No matter how much fluid is consumed, urination becomes more frequent;
- The moment the urine flows out is painful, and men will feel urethral spasm and burning pain;
- Body temperature (hyperemia) rises to a critical level.
These symptoms are quickly accompanied by a burning sensation throughout the perineum area and pain during defecation.
The indirect signs of prostate inflammation are not so obvious, but men should not ignore them:
- Ejaculation becomes too fast-the time of intercourse is reduced;
- Erection at night may take a long time;
- Loss of libido-partial or complete;
- "Flakes" or white "lines" appear in the urine.
Please note: these indirect signs indicate the very beginning of the development of the inflammatory process in question-it responds well to treatment and has no complications.
Prostatitis is divided into two courses, acute and chronic, each of which has its own characteristics.
Acute prostatitis
Acute prostatitis always starts suddenly and manifests:
- Temperature rise
- Pain in the perineum for a long period of time;
- Often want to go to the toilet;
- Release a small amount of urine and feel the bladder full.
Please note: Urinary retention is considered the most dangerous condition of the acute form of the prostate inflammatory process. In this case, men will have a strong urge to go to the toilet, but will not discharge urine even if they use too much force. Acute urinary retention is accompanied by severe pain in the anatomical area of the bladder, a kind of pressure-patients describe their condition as "now the bladder will burst". This condition requires immediate medical attention, including the use of a catheter-the catheter is inserted into the urethra and bladder, which literally means "pushing" the swollen gland. Once the catheter reached the bladder, urine began to flow out, the patient was relieved immediately, and his condition returned to normal in a short time.
Chronic prostatitis
The type of pathology under consideration is almost asymptomatic-occasionally men experience short-term pain in the perineum (similar to low back pain), noticing changes in sexual intercourse-it can be prolonged or contracted. In addition, the patient is irritable, sleepless at night, urine flow may become weak (this is due to narrowing of the urinary tract), and flaky or flaky white clots may appear in the urine in the morning. Thread.
Please note: The chronic form of the inflammatory process of the prostate may develop unknowingly. The fact is that acute prostatitis has milder symptoms when you are young. If a young man is drinking alcohol or is too enthusiastic about work, then he has no time to pay attention to changes in urination or periodic pain. perineum. The symptoms of acute prostatitis will disappear over time, but this does not mean that the disease has subsided-it just becomes a chronic disease.
Methods of treating prostatitis
The treatment of the inflammatory process of the prostate can only be carried out under the supervision of a male doctor. He not only diagnosed prostatitis itself (usually the same symptoms as prostate cancer), but also revealed the real cause of its occurrence. In general, several different therapies can be used to treat inflammation of the prostate.
medical treatement
For prostatitis, antibacterial agents (antibiotics) can be prescribed, but the premise is to isolate the pathogenic bacteria during the examination and confirm that it is the cause of the pathological development. While using antibiotics, prescribe probiotics or prebiotics-drugs that normalize the intestinal flora and resist the development of pathological processes in it.
If the inflammatory process starts due to the negative influence of external factors (hypothermia, trauma), anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs will be prescribed.
In the case of hormonal imbalance, men must receive a course of hormonal treatment.
Please note: medications vary greatly, so the choice should be based on individual circumstances-in this case self-medication is strictly prohibited.
physiotherapy
The treatment of prostate inflammation should be comprehensive. And in the context of the use of drugs, certain physiotherapy procedures can be very effective:
- Electrical stimulation-accelerates the metabolic process, stimulates more active hormone production, and restores the structure of the glands.
- Magnetic therapy is a painless procedure that helps reduce inflammation levels and eliminate prostate swelling.
- Prostate massage-only performed after medical measures have been taken for acute inflammation. The process is painful but very effective.
National Science
Please note: traditional medicine recipes should not be the only treatment method-they can only speed up the treatment process and improve the effectiveness of medication and physical therapy.
The most effective and safest alternative treatment methods include:
- Eat pumpkin seeds. They contain zinc, which is an essential element for men’s health, so for prostatitis, you need to eat 30 raw seeds 30 minutes before meals during the entire treatment.
- Pumpkin honey balls. Peel 100 grams of raw pumpkin seeds, grind them with a meat grinder (or a blender, but do not grind them into small pieces), and then mix with 200 grams of honey. Roll the resulting lumps into small balls and store them in the refrigerator. Before eating (30 minutes), you need to eat 1-2 balls-without chewing, it is better to dissolve slowly. Continue treatment with this prescription until the symptoms of prostatitis disappear.
- Hazel leaf soup. You can pick hazel leaves yourself, or you can buy dried ingredients in a pharmacy. One tablespoon of ingredients requires a cup of boiling water. The broth is brewed like ordinary tea for 20 minutes, filtered and taken at least 4 times a day, each time 50 ml. Please note: Hazel bark is also available in pharmacies-it can also be used to treat prostatitis and is used according to the same prescription. But remember, for the crust, the brewing time is doubled.
- Parsley juice. Prepared from the green leaves of the plant, 3 times a day, take 1 dessert spoon before each meal.
- Broth from parsley seeds. You need to take 1 tablespoon of parsley seeds, pour in 400 ml of boiling water, and let it stand for 2 hours (you can do this in a thermos). You need to take 1 tablespoon of broth every morning and evening.
In any case, no matter how safe the remedy seems to be, you must consult your doctor first. For example, if a man has cholelithiasis in addition to prostatitis, then he is strictly prohibited from using pumpkin seeds-any appointments are strictly based on personal circumstances.
Diet and lifestyle

In order to get the best results in treatments related to prostatitis, you need to stick to a certain diet. It should exclude fatty meat, smoked and salty dishes, pastries and chocolate from the diet. The menu can include fish and seafood, milk and its derivatives, and steamed vegetables. Using freshly prepared vegetable and fruit juices is very useful for prostatitis-they will help strengthen and restore the immune system.
During treatment, you need to abstain from alcohol and live an active lifestyle-at least, do morning exercises, walk more and get rid of excess weight.
Prostatitis is not considered a life-threatening disease in men, but ignoring its symptoms can lead to the development of serious complications. One of the most difficult consequences is male infertility and loss of erectile function, which usually occurs with long-term chronic prostatitis.